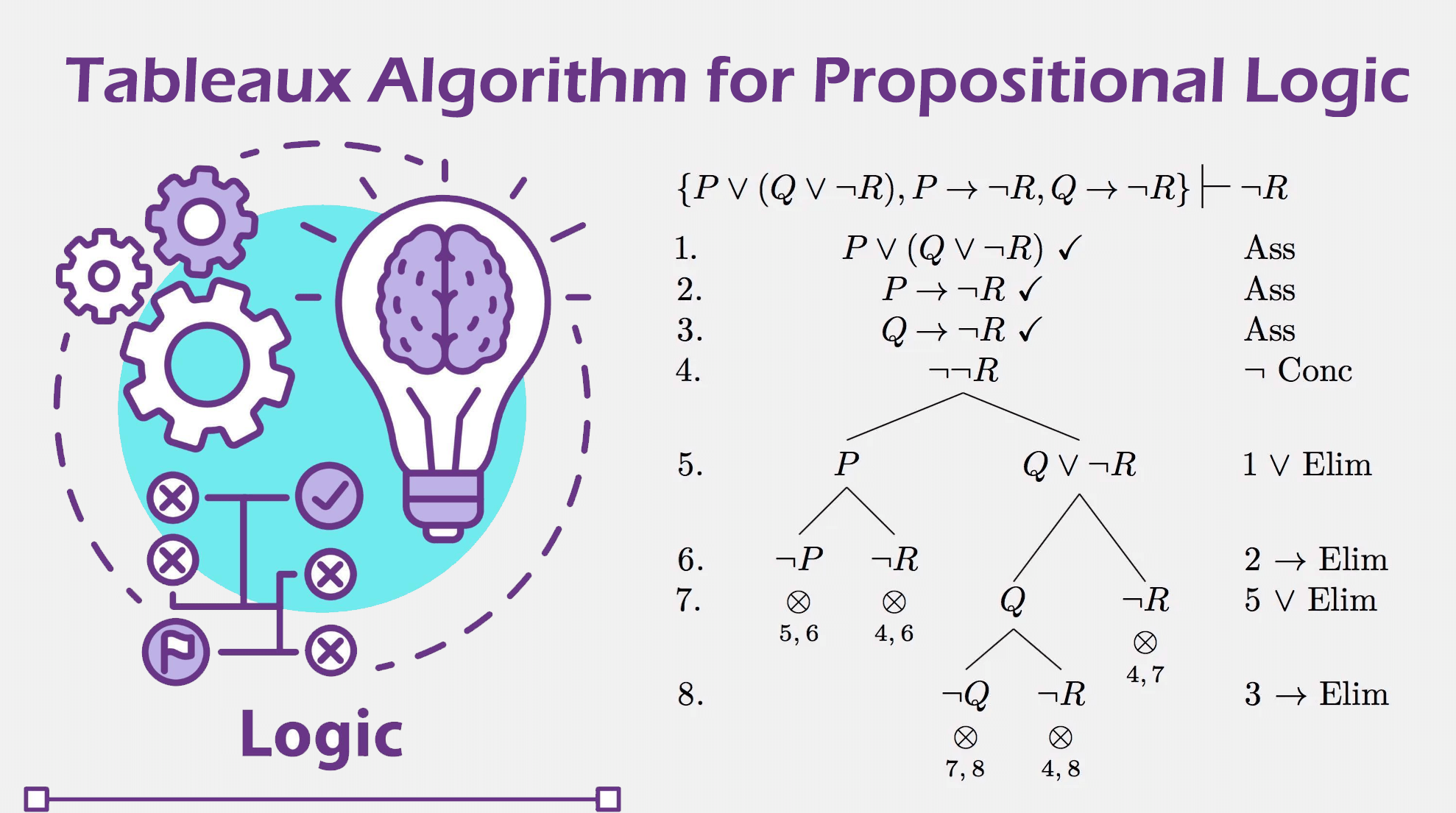
Tableaux Algorithm for Propositional Logic
This C++ program implements the Tableaux Algorithm and constructs the Tableaux Tree for Propositional Logic.
It allows you to input a propositional formula and a set of variables, and then checks whether the formula is a tautology using both
a truth table and the tableaux algorithm.
Overview
The program provides two main functionalities:
- Truth Table Validation: You can input a propositional formula and a set of variables. The program will generate a truth table and validate whether the formula is a tautology.
- Tableaux Algorithm: The program also implements the Tableaux Algorithm. It negates the input formula, constructs the Tableaux Tree, and checks whether it’s closed. If the tree is closed, the input formula is a tautology.
Usage
Input: When prompted, enter your propositional formula (with no space) using the following symbols:
~ for negation
^ for conjunction (AND)
v for disjunction (OR)
> for implication
Enter Variables: After entering the formula, input the variables used in the formula. Enter each variable followed by pressing Enter. To finish, enter -.
Validation: The program will first validate the formula using a truth table and tell you whether it’s a tautology.
Tableaux Algorithm: Then, it will apply the Tableaux Algorithm, construct the Tableaux Tree, and check whether the tree is closed.
Examples
Here are some example inputs and outputs:
Example 1:
Input Formula: (p^q)>(q^p)
Variables: p q
Output: “This proposition is a tautology.”
Example 2:
Input Formula: ((p^q)v(~r>s))>(r^(pv~q))
Variables: p q r s
Output: “This proposition is not a tautology.”