Coding 5 Tree – Solving Weighted Maze by Dijkstra
Tree Coding!
Join us on this educational journey through the world of data structures and discover the elegance and utility of Red-Black Trees, AVL Trees, Huffman Code Trees, Min Heaps, and B-Trees.
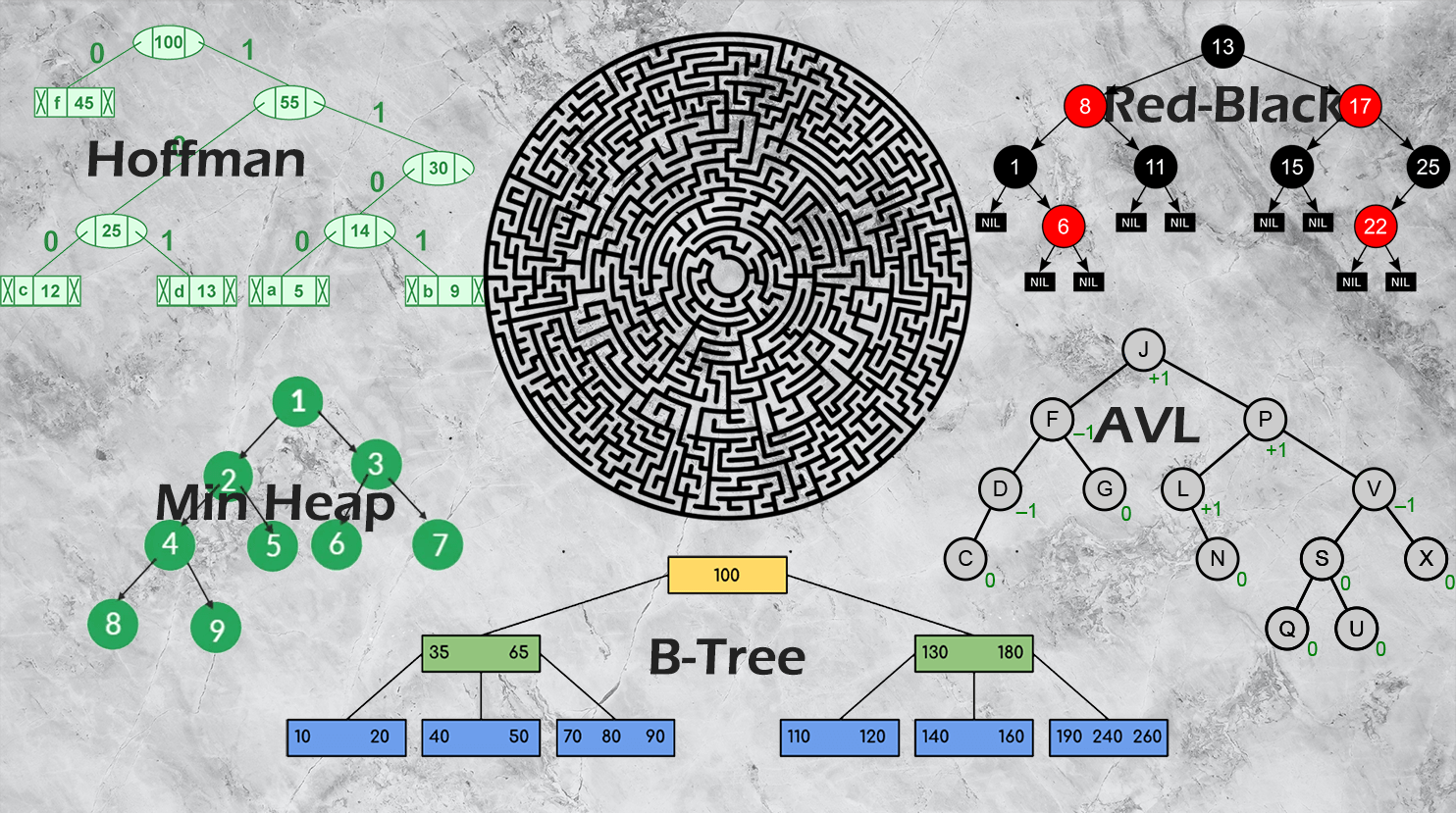
Red-Black Tree
🔴⚫️ The Red-Black Tree is a self-balancing binary search tree known for its efficiency and balance. Its striking red and black nodes maintain a harmonious structure, ensuring that the tree remains balanced, and operations like insertion and deletion are performed optimally. Discover the beauty of Red-Black Trees and their critical role in maintaining balanced data structures.
AVL Tree
🌳 The AVL Tree, named after its inventors Adelson-Velsky and Landis, is another self-balancing binary search tree. Its remarkable self-balancing property guarantees that the tree remains height-balanced, leading to efficient searching and retrieval of data. Dive into the world of AVL Trees and understand how they maintain equilibrium in data structures.
Huffman Code Tree
📜 The Huffman Code Tree, an essential concept in data compression, allows us to represent data efficiently by assigning shorter codes to more frequent symbols. Explore the construction of Huffman Trees and witness their magic in encoding and decoding data, saving space while preserving information.
Min Heap
⬇️ Heap data structures are vital for efficient priority queue implementations. The Min Heap, in particular, ensures that the smallest element is always at the root. Learn about the mechanics of Min Heaps and how they enable quick access to the minimum element, making them invaluable in algorithms like Dijkstra’s and heapsort.
B-Tree
🌲 The B-Tree is a versatile data structure designed for handling large datasets efficiently. Its balanced structure and branching factor make it ideal for organizing data in databases and file systems. Uncover the power of B-Trees in managing and searching vast amounts of information.
Maze Solver
This C++ program is designed to solve mazes using a B-Tree data structure.
It efficiently finds the shortest path in a maze using Dijkstra’s algorithm and provides a visualization of the solution.
B-Tree Implementation
The B-Tree is a self-balancing tree structure that ensures efficient insertion and deletion of elements. In this program, the B-Tree is used to manage the cells in the maze efficiently. When the program explores a new cell, it inserts it into the B-Tree. If it finds a shorter path to a cell it has already explored, it updates the cell’s information in the B-Tree.
The B-Tree implementation includes functionalities for insertion, deletion, and balancing to maintain optimal performance throughout the maze-solving process.
Usage
The first line specifies the dimensions of the maze (rows and columns).
Subsequent lines represent the maze grid, where each number indicates the weight of a cell.
View the Solution: The program will solve the maze and display the solution, including the shortest path from the start to the end. Obstacles are indicated by 0, and the path is marked with -1.
Explore Further: Feel free to experiment with different maze configurations and weights to see how the program efficiently finds the shortest path.